A new Systematic Review has been published on the Archives of Public Health website titled “Effectiveness of smoking cessation on the high-risk population of lung cancer with early screening: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials until January 2022“. Not exactly catchy!
You can also download the PDF and Epub versions of this too.
I will only summarise the main points – read the full study for further info!
Background
Lung cancer has always been linked to smoking and those who are at risk of developing this disease have been observed for this review.
The study wanted to see the efficiency of different methods of stop smoking intervention and the safety of those methods.
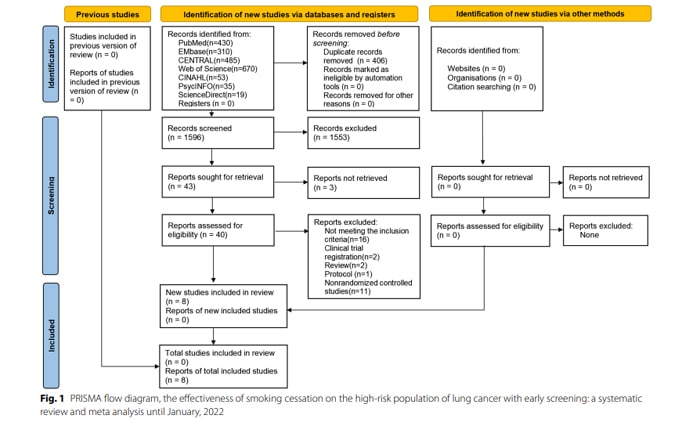
Various studies were found and screened for use in this review from various databases including PubMed, Science Direct, Embase, Web of Science etc.
The 7 day point of quitting smoking was evaluated and they also examined the possibility of continuing to stay away from cigarettes.
The 998 participants aged from 57-63 were from many countries including USA, Italy, Canada, Australia and UK.
Results
There is quite a lot of data here but the main summary is that using e-cigarettes showed 1.51 times more efficiency in quit smoking attempts than other interventions.
Conclusion
The participants were long-term smokers who undergo Low-Dose Computed Tomography screening. This is a type of lung scan also known as a LDCT or Low-Dose CT Scan.
These screening processes can help those at risk of Lung Cancer become aware of the dangers of continuing smoking and any negative effects the habit is having.
It is believed by some researchers that this screening process can instigate smoking cessation as it brings home the risk of continuing smoking to the patients’ health.
The main interventions to help these people stop smoking were behavioural / psychological intervention or e-cigarettes (Pharmacological).
I quote…
“The results of this study show that E-cigarettes support people at high risk of lung cancer to quit smoking in the short term, which is consistent with the results of Harrell et. al. However, despite their ability to aid in quitting smoking, e-cigarettes can cause unwanted respiratory side effects as cough, nauseousness, and dyspnea. Therefore, it is advised that clinical practice should make a wise decision to stop smoking based on thoroughly assessing its smoking cessation effect and negative effects. Because the study included in this systematic review only followed up on the effect of E-cigarettes for 6 months, therefore we were unable to determine the effect of e-cigarettes over the long term. Future research is hoped to follow up on the long-term effects of e-cigarettes and thus evaluate the long-term effects of quitting smoking.”
All in all so far is showing to be quite positive for swapping smoking for vaping – which is great to see.
The side effects quoted could also be found in anyone quitting smoking regardless of e-cigarette use – that is just my opinion though!
The study ends with…
“In conclusion, the results of this systematic review show that smoking cessation intervention is effective for long-term lung cancer high-risk smokers who participate in early screening. Among them, E-cigarettes are the best, followed by individual smoking cessation.”
👉 “The results of this systematic review show that smoking cessation intervention is effective for long-term lung cancer high-risk smokers who participate in early screening, of which #Ecigarettes are the best, followed by individual smoking cessation.”https://t.co/ENXEzc63xx
— IEVA (@europeanvaping) June 13, 2023
The results of this systematic review show that smoking cessation intervention is effective for long-term lung cancer high-risk smokers who participate in early screening, of which E-cigarettes are the best, followed by individual smoking cessation. @CANSAhttps://t.co/O5Xuv7Dtif
— Kurt Yeo (@Kurt_Yeo) June 13, 2023