To vape safely you need to understand a couple of basics about electricity
You will come across the terms VOLTS, Current, AMPS, Resistance, OHMS, Power and WATTS. In this guide we explain what these mean in terms of vaping.
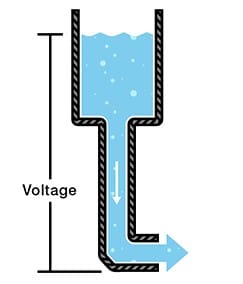
Voltage, volts, V.
Typically, a fully charged battery will read that it has around 4.2V – 4.2volts
This can be understood as the amount of oomph pushing the electricity through your coil, vaporizing the e liquid.
You can think about it being like water pressure. As the quantity of water drains from the tank there is less water left, the ‘push’ gets smaller and the flow reduces.
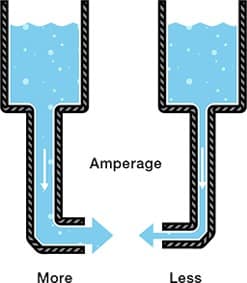
Current, amps, A
The current is the ‘flow’ of electricity.
The faster it flows the quicker the battery drains.
Also, the faster it flows the hotter the coil in your atomizer gets, vaporizing more e-liquid.
A variable wattage/voltage device will keep the current flowing at a constant rate by ‘pushing’ it.
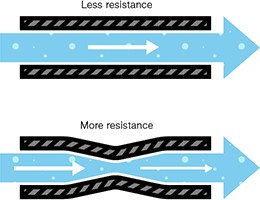
Resistance, ohms, Ω
Increasing the resistance slows down the flow of electricity.
This can give a cooler vape.
This is achieved by using thinner wire but this means that there is less wire touching the wick and can also reduce flavor and vapor production.
Lower resistance is used by having thicker wire or flat wire, often used by people using rebuild-able atomizers.
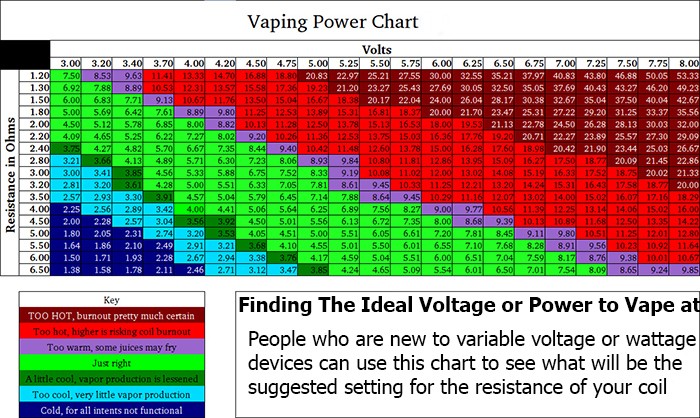
Ohms Law
To work out the maximum current flowing through your coil divide 4.2 by the resistance value of the coil you are using.
To calculate what coil to build divide 4.2 by the maximum current the battery will withstand (ask your vendor).
Power, watts
Power is the rate energy is transferred from the battery to your coil.
Many people use the variable wattage setting on their device as this gives a consistency to the vape as the battery loses charge.